I. Definition and Purpose of Weight Loss Clinics
A. What are Weight Loss Clinics?
1. Definition
– Facilities or organizations focused on helping individuals lose weight.
– Offer a combination of medical, nutritional, and behavioral support.
2. Structure and Operation
– Typically staffed by healthcare professionals, including doctors, nutritionists, and fitness trainers.
– May operate in various settings, including hospitals, private practices, or specialized centers.
B. Goals of Weight Loss Clinics
1. Weight Management
– Help clients achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
– Focus on gradual, sustainable weight loss rather than quick fixes.
2. Health Improvement
– Reduce the risk of obesity-related diseases (e.g., diabetes, hypertension).
– Improve overall physical health and well-being.
3. Behavioral Change
– Teach clients how to modify their eating and exercise habits.
– Promote a healthier lifestyle that can be maintained long-term.
4. Emotional Support
– Provide psychological support to address emotional eating and body image issues.
– Foster a supportive environment to encourage accountability and motivation.
C. Target Audience
1. Individuals Struggling with Weight Management
– Adults, teens, and children dealing with obesity or overweight issues.
2. Those Seeking Professional Guidance
– Individuals who prefer structured programs rather than self-directed efforts.
3. Patients with Related Health Issues
– People with conditions such as metabolic syndrome, heart disease, or joint problems requiring weight loss.
D. Overall Impact
1. Community Health
– Contribute to public health efforts by addressing obesity trends.
– Promote awareness and education around healthy lifestyle choices.
2. Quality of Life Improvement
– Enhance clients’ physical and mental well-being.
– Empower individuals to lead healthier, more active lives.
This outline provides a structured overview of what weight loss clinics are, their purpose, and their overall impact on individuals and the community.
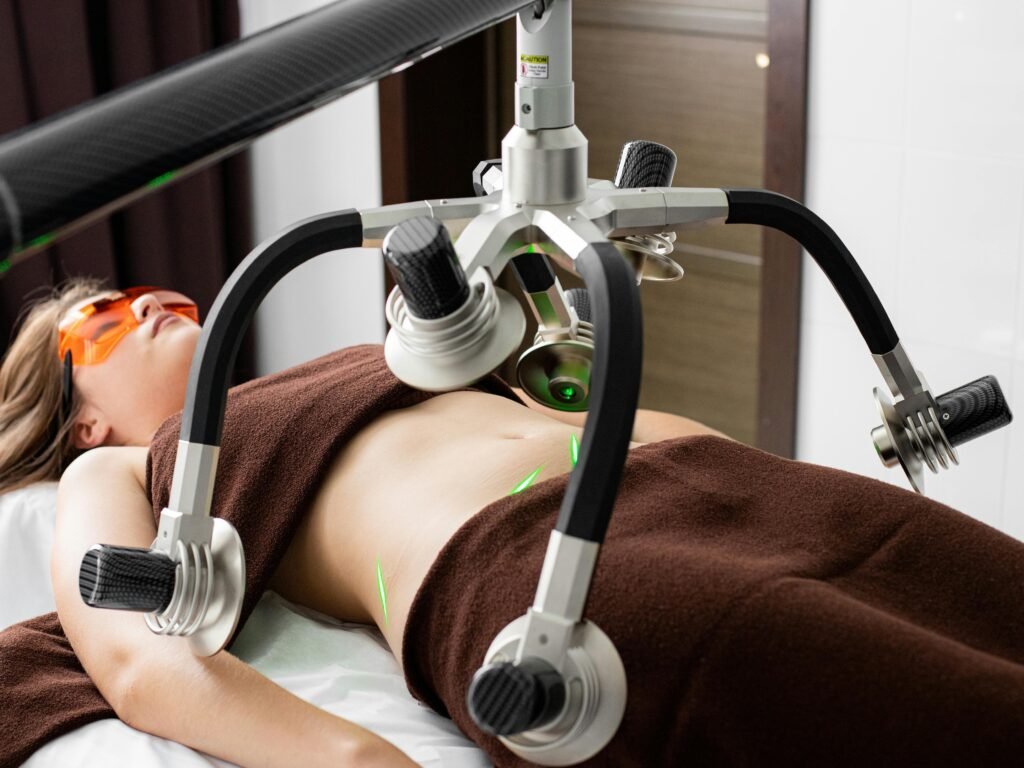
:
II. Types of Weight Loss Clinics
A. Medical Weight Loss Clinics
1. Definition and Focus
– Medical-personnel-operated clinics, including doctors and registered dietitians.
– Medically directed weight loss methods.
- **Services Offered **
Full health check-ups, including metabolic testing and blood work
Medications or supplements to help lose weight
Individualized meal plans and workout plans based on medical history. - Target Market
– Individuals with health conditions related to obesity.
– Individuals who, for health reasons, need medical intervention to lose weight safely. B. Holistic and Wellness Clinics- **Definition and Approach
- Emphasize general health, rather than pure weight loss, by including physical, mental, and emotional well-being. – Include natural and alternative therapies that complement traditional weight loss techniques.
- Services Offered
- Nutritional counseling, with emphasis on whole foods and balance of diets.
Mindfulness practices, stress management, and lifestyle coaching.
Group therapy sessions and community support networks.
- Nutritional counseling, with emphasis on whole foods and balance of diets.
- Services Offered
- Target Audience
Those who are looking for an integrated health service.
- People desiring to lose weight naturally and organically.
C. Specialty Weight Loss Programs
- Bariatric Clinics
• Include various surgeries for weight loss, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy.
- Pre-operative assessments and post-operative care.
- Lifestyle-Focused Programs
- Targeted toward specific sectors of the population, such as children, adolescents, seniors, or professional athletes.
- Special programs aimed at the particular needs and problems within these categories.
- Lifestyle-Focused Programs
- Corporate Weight Loss Programs
• On-site workplace programs are available to make employees healthier.
• On-site counseling, exercise classes, and weight loss challenges may be offered. D. Virtual and Online Weight Loss Clinics- **Definition and Growth
- Telehealth and web-based facilities offering remote facilities.
• Accessibility facilitated by advances in technology.- Services Offered
• Virtual consultation with a dietitian and fitness coach.
Access to digital resources, meal plans, and fitness apps.Target Market
For some individuals, in-person clinics are not accessible.
Individuals want flexibility in terms of scheduling and location.
- Services Offered
- Success Rates and Effectiveness – The comparison of the outcomes between clinic types.
- Cost and Insurance Coverage
- How pricing and acceptance may vary from clinic to clinic.
- Personal Preferences and Needs
- Cost and Insurance Coverage
- Importance of finding a clinic that will match individual goals and values.
This outline gives an overview of the different kinds of weight loss clinics, their methodologies, and services offered, along with the intended target audience, which helps in bringing some clarity into the diverse options available for those in search of professional support in weight management.
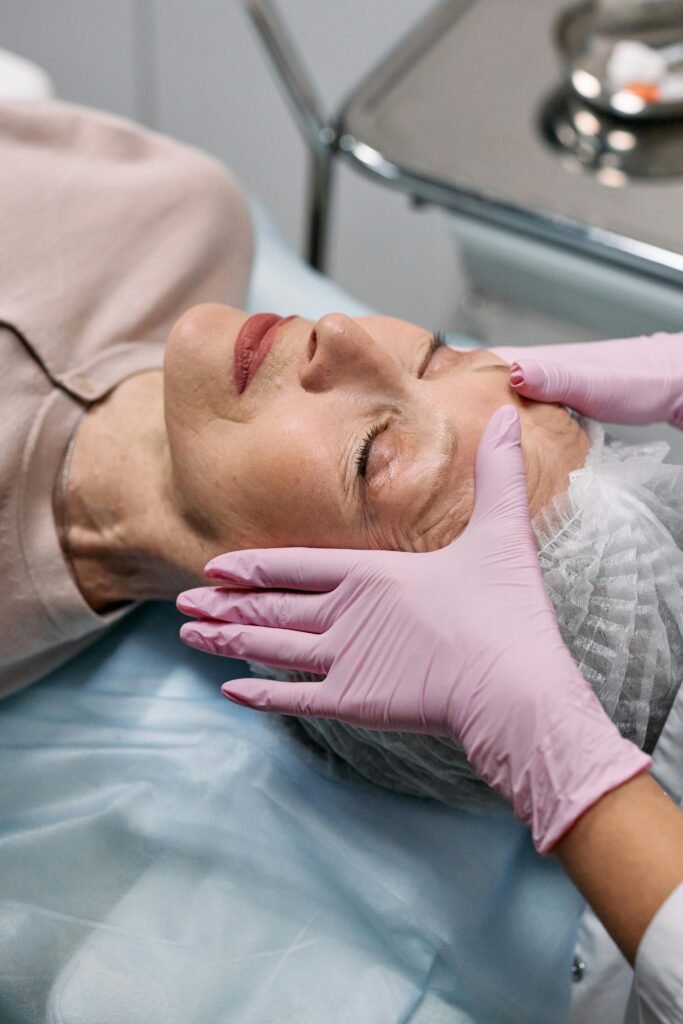
III. Fitness Level Assessment
A. Reasons for Initial Assessment
1. Baseline Understanding of Fitness Level
– Establishing a starting point for individual fitness levels.
- Identifying strengths and weaknesses.
- Exercise Program Development
- Design adaptation of exercise programs to the capability of the individual.
- Appropriateness and safety of exercises for each client.
- Exercise Program Development
- Physical Health Assessment
– Past medical history and present complaints.
– General health checkups.- Body Composition Analysis
- Percentage of body fat, muscles, and BMI.
Measurements by tools such as calipers, bioelectrical impedance, or DEXA scans.
- Percentage of body fat, muscles, and BMI.
- Cardiovascular Fitness Testing
Assess the efficiency of the heart and lungs in tests that may include a treadmill test or VO2 max testing.
Assess endurance levels or the capacity for aerobic exercise.
- Body Composition Analysis
- Tests for Muscle Strength and Flexibility
– Assessment of upper and lower body strength can be done by exercise, such as push-ups and squats.
– Specific tests, like the sit-and-reach, can be used to diagnose flexibility.- **Functional Movement Screening
Making assessment of the various movement patterns for limitations or imbalance.
Emphasizing functionality to execute daily activities effectively
- **Functional Movement Screening
- Setting Realistic Fitness Goals
- SMART Goals Framework
- Encouragement of SMART goals.
- Short-term vs. Long-term Goals
- Discriminate between immediate fitness milestones versus ultimate weight loss objectives.
- Client Involvement in Goal Setting
-Enable the client to take responsibility for his or her own exercise program.
-Elaboration of personal reasons and preferences.
- Integrating Assessment Findings
Results from fitness assessments to develop an appropriate exercise plan. - Types of Exercise
Cardiovascular, strength, and flexibility exercises
Need variation to hold the attention and motivation of each client.
- Short-term vs. Long-term Goals
- Progressive Overload Principle
– Increase the intensity and volume gradually.
– The clients should be challenged adequately without running the risk of injury. E. Importance of Ongoing Assessment and Adjustments- Regular Check-ins
- Besides, schedule periodic fitness assessments for progress tracking. – Change the fitness plans according to the improvement and shifting goals.
- Feedback Mechanisms
- Encourage clients to give feedback about workouts and experiences.
- Feedback Mechanisms
- Utilizing feedback for furthering the efficiency of the programs of fitness.
- Update/Change Goals
- Adjusting goals and plans of fitness according to the progress and obstacles faced by the person.
- Celebration of successes in order to motivate and create confidence Weight Loss Clinic.
- Update/Change Goals
